The correct answer is Option (3) → (A) - (I), (B) - (II), (C) - (IV), (D) - (III)
|
List-I (Stage of Demographic Transition)
|
List-II (Country/Tribe)
|
|
(A) High Fluctuating Stage
|
(I) Rainforest tribes
|
|
(B) Early Expanding Stage
|
(II) Angola
|
|
(C) Low Fluctuating Stage
|
(IV) Japan
|
|
(D) Late Expanding Stage
|
(III) India
|
-
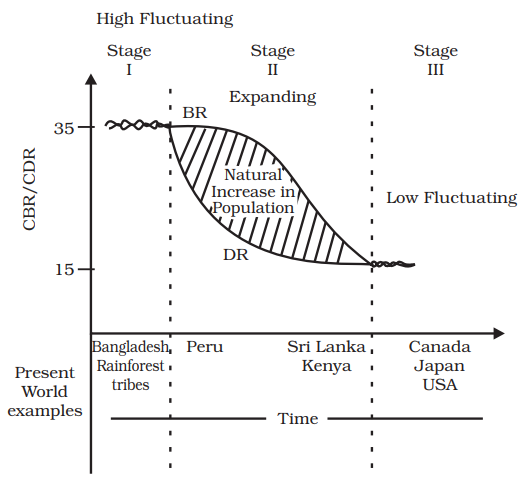
(A) High Fluctuating Stage - (I) Rainforest tribes:
- In this stage, both birth rates and death rates are high and fluctuate due to factors like disease, famine, and high infant mortality. This stage is typical of traditional societies, such as rainforest tribes, where subsistence living is common and healthcare is limited.
-
(B) Early Expanding Stage - (II) Angola:
- The early expanding stage is characterized by high birth rates and declining death rates, leading to population growth. Countries like Angola, with high fertility rates and improving healthcare, fit this description as they experience significant population increases due to improved living conditions and medical advances.
-
(C) Low Fluctuating Stage - (IV) Japan:
- In the low fluctuating stage, both birth rates and death rates are low, resulting in a stable population. Japan is a prime example, as it has low fertility rates and a long life expectancy, leading to a mature demographic profile where the population is stable or declining.
-
(D) Late Expanding Stage - (III) India:
- The late expanding stage shows a decline in birth rates following a previously high birth rate, while death rates remain low. India is in this stage, where population growth continues but at a slowing rate due to changing societal norms, increased education, and healthcare access, contributing to lower fertility rates over time.
|