The correct answer is option 3. Accelerate the rate of reaction.
A catalyst is a substance that participates in a chemical reaction, but it is not consumed or permanently altered by the reaction itself. Instead, it provides an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy. Activation energy is the energy barrier that reactant molecules must overcome for the reaction to occur.
By providing this lower-energy pathway, a catalyst facilitates the breaking and forming of chemical bonds in the reactant molecules. This allows the reaction to proceed at a faster rate compared to the uncatalyzed reaction.
To understand how a catalyst accelerates the rate of reaction, consider the energy diagram of a typical reaction:
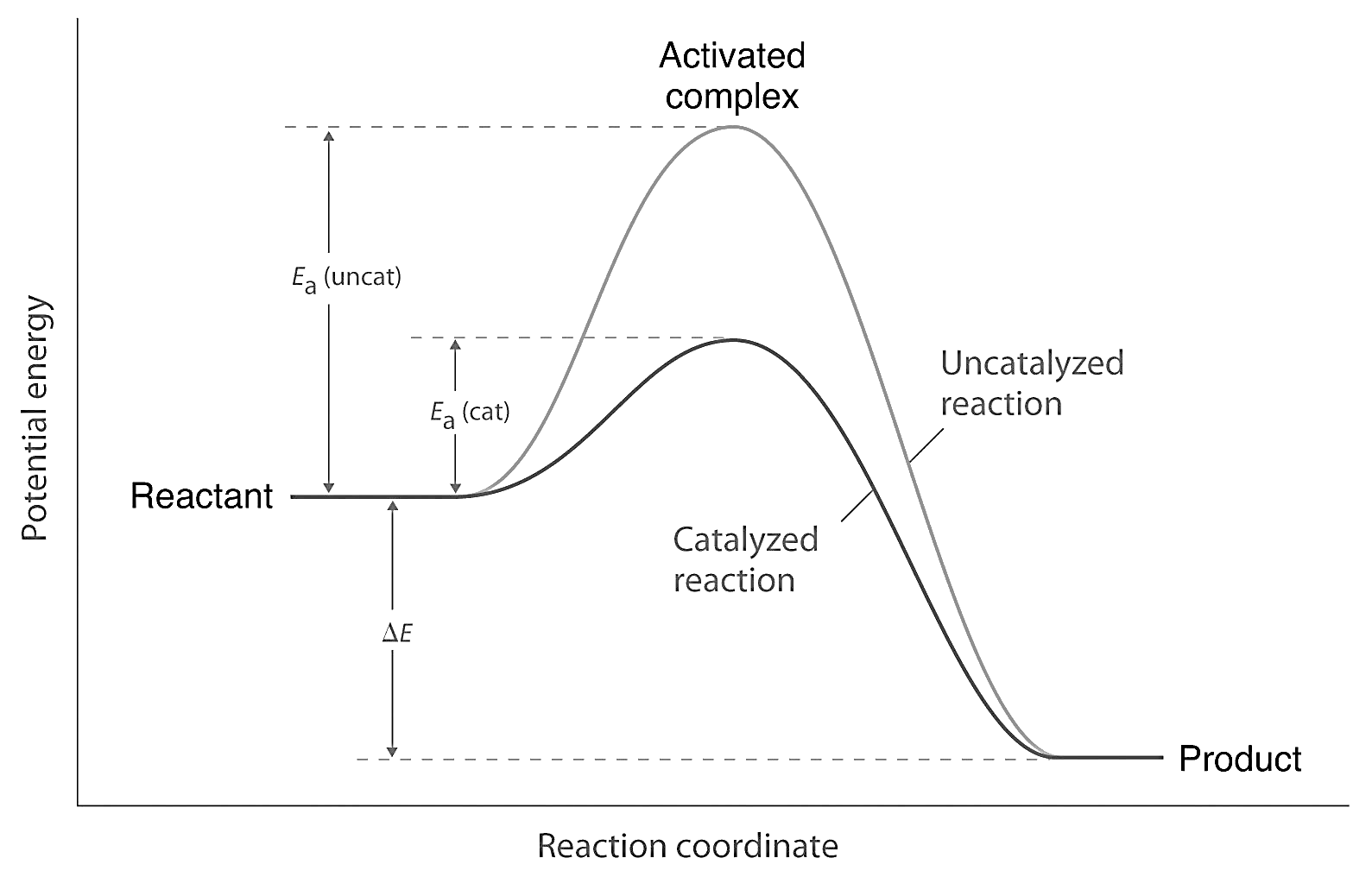
In the presence of a catalyst, the activation energy required for the reaction is reduced. This is represented by the lower peak on the energy diagram. As a result, a larger fraction of reactant molecules now possess sufficient energy to overcome the lower energy barrier and proceed to the product state.
By lowering the activation energy, the catalyst enables more reactant molecules to successfully undergo the reaction, leading to an increased rate of the reaction. However, it's important to note that a catalyst does not alter the thermodynamics of the reaction or change the final equilibrium position or the amount of product formed. It only speeds up the attainment of equilibrium by accelerating the forward and reverse reactions to the same extent.
Catalysts themselves are not consumed during the reaction, so they can participate in multiple reaction cycles. They can be present in small amounts relative to the reactants and can often be reused, making them highly efficient and cost-effective in industrial processes.
In summary, the function of a catalyst in a chemical reaction is to lower the activation energy, provide an alternative reaction pathway, and accelerate the rate of the reaction without being consumed in the process. |