Reasoning: "Change in quantity supplied is of two types- Extension of Supply and Contraction of Supply." This is correct. Extension and contraction of supply are indeed the two types of changes in quantity supplied, and they are directly related to changes in the price of the commodity.
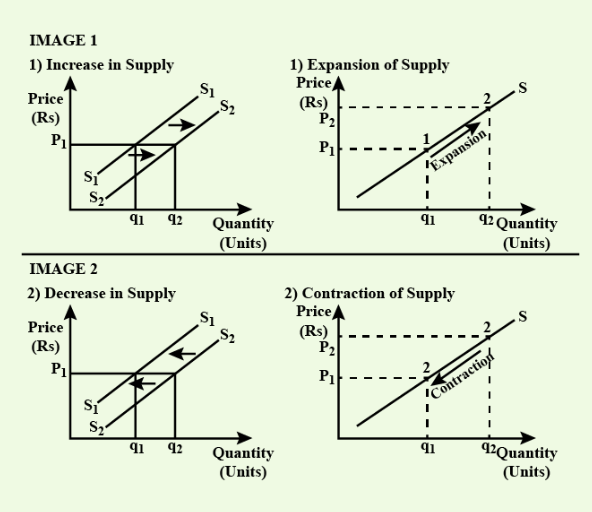
1. When quantity supplied of a commodity changes due to change in its own price, assuming, other things being equal, it is known as change in quantity supplied. It is represented by movement along the same supply curve. It is of two types:
a. Extension/Expansion of Supply: This refers to the movement along the existing supply curve. It occurs when the price of a commodity increases, and as a result, the quantity supplied also increases, with all other factors remaining constant. For example, supply of tea increases due to rise in its prices, other things being equal.
b. Contraction of Supply:This refers to a movement along the existing supply curve. It occurs when the price of a commodity decreases, and as a result, the quantity supplied also decreases, while all other factors remain constant. For example, supply of tea decreases due to fall in its prices, other things being equal.
2. When supply of a commodity changes due to changes in other factors than price of the commodity, it is known as change in supply. For example, change in supply of a commodity due to change in technology etc. It is of two types:
a. Increase in Supply:This refers to a shift of the entire supply curve to the right. It occurs when factors other than the price of the commodity (e.g., technology, input costs) change, leading to a greater quantity supplied at every price level. For example, there is improvement in technology which reduces the cost of production of Hitachi ACs, leading to an increase in the supply of ACs at every price level.
b. Decrease in Supply:This is where the entire supply curve shifts to the left. This occurs when factors other than the price of the item change. For example, if the technology used to manufacture Hitachi ACs deteriorates (becomes outdated or less efficient), fewer ACs will be supplied at every price level, causing a decrease in supply.