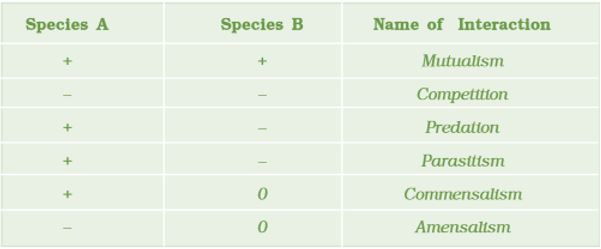
The correct answer is Option (3)-
|
Species A
|
Species B
|
Name of interaction
|
|
-
|
-
|
Predation
|
Competition is best defined as a process in which the fitness of one species (measured in terms of its ‘r’ the intrinsic rate of increase) is significantly lower in the presence of another species. It is relatively easy to demonstrate in laboratory experiments, as Gause and other experimental ecologists did, when resources are limited the competitively superior species will eventually eliminate the other species, but evidence for such competitive exclusion occurring in nature is not always conclusive. Connell’s elegant field experiments showed that on the rocky sea coasts of Scotland, the larger and competitively superior barnacle Balanus dominates the intertidal area, and excludes the smaller barnacle Chathamalus from that zone.
Mutualism: This interaction confers benefits on both the interacting species. Lichens represent an intimate mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthesising algae or cyanobacteria. Similarly, the mycorrhizae are associations between fungi and the roots of higher plants. The fungi help the plant in the absorption of essential nutrients from the soil while the plant in turn provides the fungi with energy-yielding carbohydrates.
Parasitism is generally defined as a relationship between the two living species in which one organism is benefitted at the expense of the other. The organism that is benefitted is called the parasite, while the one that is harmed is called the host. Endoparasites are those that live inside the host body at different sites (liver, kidney, lungs, red blood cells, etc.)
In amensalism one species is harmed whereas the other is unaffected. Predation, parasitism and commensalism share a common characteristic– the interacting species live closely together.
|