The correct answer is Option (3) -(C), (A), (D), (B)
PCR is a laboratory technique that allows the selective amplification of a specific DNA sequence in vitro, outside of a living organism.
Each cycle of polymerase chain reaction has three steps. They are:
- Denaturation: The first step in PCR is denaturation. Denaturation is required to separate the double-stranded DNA sample. It is done at 94-98 ℃ for 20-30 seconds. It breaks the hydrogen bonds present between base pairs. Denaturation leads to the formation of single strands of DNA.
- Annealing: The second step is the annealing of the primer. Here the reaction temperature is lowered to allow the complementary base pairing between the primer and the complementary part of the single strands of the DNA template. A proper temperature needs to be maintained in order to allow highly specific and proper primer hybridisation. Then DNA polymerase binds to the template-primer hybrid and starts the DNA synthesis.
- Extension: A thermostable DNA polymerase is used for this purpose. Taq polymerase is commonly used for this purpose. It is done at a temperature of 75-80 ℃ (72℃). The DNA polymerase adds nucleotides in the 5’-3’ direction and synthesises the complementary strand of the DNA template.
-
After several cycles of denaturation, annealing of primers, and extension of primers, the target DNA sequence is exponentially replicated. The extension step, facilitated by a DNA polymerase enzyme, synthesizes new DNA strands complementary to the template strands, using the primers as starting points.
As PCR cycles progress, the number of copies of the target DNA sequence doubles with each cycle, leading to a significant increase in the amount of DNA. This accumulation of DNA copies is what we refer to as "amplified DNA."
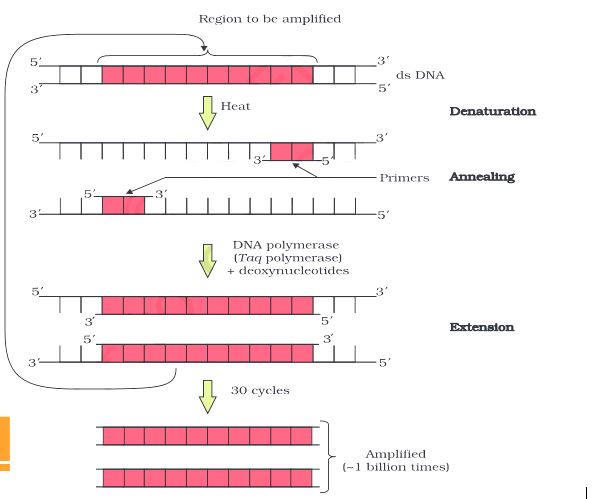
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) : Each cycle has three steps: (i) Denaturation; (ii) Primer annealing; and (iii) Extension of primers
|