The correct answer is option 4. \(KMnO4 – KOH/Δ, HCl\).
The conversion of alkylbenzenes to carboxylic acids involves a series of oxidation reactions. The specific reagent \(KMnO_4 – KOH/Δ, HCl\) is commonly used for this purpose. Let's break down the reaction mechanism:
1. Formation of Benzoic Acid (Phenylmethanoic Acid):
The general reaction for the conversion of an alkylbenzene to a carboxylic acid involves the oxidation of the side chain to a carboxylic acid group. The manganese(VII) ions in potassium permanganate (\(KMnO_4\)) are a strong oxidizing agent.
The overall equation for the reaction is:
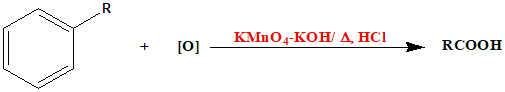
Here, \(R\) represents the alkyl group attached to the benzene ring.
2. Reaction Conditions:
\(KMnO_4\) is used in the presence of \(KOH\) (potassium hydroxide) and heat (\(Δ\)) in the initial step.
The mixture is then acidified with \(HCl\) to complete the reaction.
3. Mechanism:
The reaction involves the oxidative cleavage of the carbon-carbon bonds in the alkyl side chain. The manganese(VII) ions in permanganate undergo reduction to manganese(IV) oxide (\(MnO_2\)).
The mechanism is quite complex and involves multiple steps, including the formation of intermediate species and the generation of carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)) as a byproduct.
4. Balancing the Equation:
The specific conditions of the reaction (\(KMnO_4 – KOH/Δ, HCl\)) are crucial for the successful oxidation. The balanced equation can be represented as:
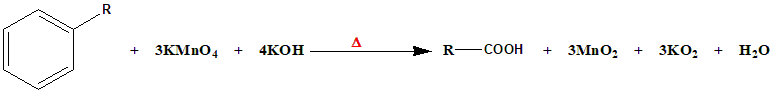
The excess \(KMnO_4\) is often reduced to \(MnO_2\) during the reaction.
In summary, the reaction using \(KMnO_4 – KOH/Δ, HCl\) is a powerful method for converting alkylbenzenes into carboxylic acids by oxidizing the side chain. This method is widely employed in organic chemistry for the synthesis of carboxylic acids from various starting materials. |